Tax planning in India involves strategic financial management to optimize tax liabilities while complying with relevant tax laws. This includes utilizing tax-saving investments such as Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS), Public Provident Fund (PPF), and National Pension System (NPS), as well as maximizing deductions available under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act. Additionally, taxpayers can leverage tax benefits on home loans, charitable contributions, and timing investments to minimize tax outflows. Consulting with tax professionals can provide personalized guidance for effective tax planning tailored to individual financial situations.
What is importance of Tax planning in India ?
Tax planning in India holds immense importance as it allows individuals and businesses to strategically manage their finances while minimizing their tax liabilities within the framework of the law. By taking advantage of various deductions, exemptions, and tax-saving investments provided under the Income Tax Act, taxpayers can optimize their financial resources, enhance cash flow, and ensure compliance with legal requirements. Effective tax planning not only facilitates the achievement of long-term financial goals, such as retirement planning and wealth accumulation, but also supports government initiatives aimed at promoting economic growth and financial inclusion. Moreover, tax planning empowers individuals with greater control over their financial affairs, enabling them to make informed decisions and secure their financial future while mitigating risks and maximizing opportunities for growth and prosperity.
Type of taxes in India ?
In tax planning in India, various types of taxes are considered, including:
Income Tax:
Income tax is levied on the income earned by individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs), companies, and other entities. Tax planning strategies aim to minimize taxable income through deductions, exemptions, and tax-saving investments.
Capital Gains Tax:
Capital gains tax is imposed on the profits earned from the sale of capital assets such as stocks, real estate, and mutual funds. Tax planning involves strategies to optimize capital gains tax liability, including holding assets for the long term to qualify for lower tax rates or utilizing exemptions available under the Income Tax Act.
Goods and Services Tax (GST):
GST is a value-added tax levied on the supply of goods and services. Tax planning strategies focus on minimizing GST liabilities through proper classification of transactions, availing of input tax credits, and complying with GST filing requirements.
Corporate Tax:
Corporate tax is imposed on the profits earned by companies registered in India. Tax planning for corporations involves structuring business operations, utilizing tax incentives and exemptions, and optimizing tax deductions to minimize corporate tax liabilities.
Securities Transaction Tax (STT):
STT is imposed on transactions involving the purchase or sale of securities such as stocks and derivatives. Tax planning strategies may include timing transactions to minimize STT liabilities or choosing investment avenues with lower tax implications.
Customs Duty:
Customs duty is imposed on the import and export of goods. Tax planning strategies aim to optimize customs duty payments through duty drawback schemes, exemptions, and concessions available under international trade agreements.
What are the steps involved in filing Income Tax Returns (ITR) in India?
1. Gather Documents:
Collect all necessary documents, including PAN card, Aadhaar card, bank statements, Form 16 (if salaried), details of income from other sources, investment proofs, and relevant tax-saving documents.
2. Choose the Right ITR Form:
Select the appropriate ITR form based on your sources of income and filing status. Commonly used forms include ITR-1 (Sahaj) for individuals with income from salary, house property, and other sources, and ITR-2 for individuals and HUFs with income from capital gains or foreign assets.
3. File Online or Offline:
You can file your ITR online through the Income Tax Department's e-filing portal (https://www.incometaxindiaefiling.gov.in) or offline by submitting a physical copy of the filled ITR form at the designated income tax office.
4. Register on the E-filing Portal:
If filing online, register on the Income Tax Department's e-filing portal using your PAN card. If you are already registered, log in with your credentials.
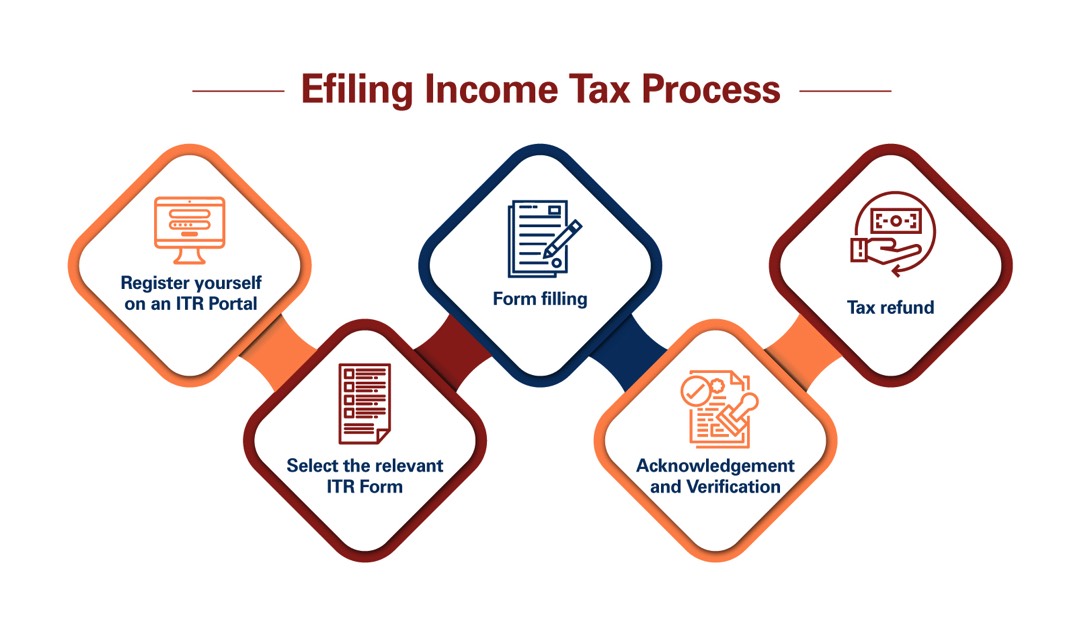
5. Fill Out the ITR Form:
Fill out the ITR form accurately with details of your income, deductions, and taxes paid. Use the Form 16, Form 26AS, and other documents to ensure accuracy.
6. Verify Your Return:
After filing the ITR online, verify it using any of the available options such as Aadhaar OTP, net banking, or sending a signed physical copy (ITR-V) to the Centralized Processing Center (CPC) within 120 days of filing.
7. E-verify Your Return:
Alternatively, you can e-verify your return online using options such as Aadhaar OTP, net banking, bank account number, or Demat account number.
8. Acknowledgment:
Once the ITR is successfully verified, an acknowledgment receipt or an acknowledgment number is generated. Keep this for your records as proof of filing.
9. Monitor Processing:
Keep track of the status of your filed return on the e-filing portal. You can check the status of processing, refund status, and any notices issued by the Income Tax Department.
10. Respond to Notices:
If you receive any notices or communications from the Income Tax Department regarding your filed return, respond promptly with the required information or documents.





